Medication vs Therapy: Which Works Better for Anxiety?
Anxiety affects millions of people worldwide, and one of the most common questions is whether medication or therapy works better for anxiety. Both options are widely used, medically approved, and effective — but they work in very different ways. Understanding the differences can help you make a calmer, more informed decision.
In this guide, we compare medication vs therapy for anxiety, including benefits, risks, long-term effectiveness, and what mental health experts recommend.
Understanding Anxiety Treatment Options
Anxiety disorders occur when fear, worry, or nervousness become persistent and interfere with daily life. Common conditions include generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), panic disorder, social anxiety, and health anxiety.
Treatment usually focuses on reducing symptoms, improving daily functioning, and preventing relapse. The two most common approaches are medication and therapy — sometimes used alone, and often combined.
You may also want to read our detailed guide on
different types of anxiety disorders and their symptoms.
Medication for Anxiety: Benefits and Limitations
Medication helps manage anxiety symptoms by affecting brain chemicals related to mood, fear, and stress response. Doctors typically prescribe anxiety medication when symptoms are severe or interfere significantly with daily life.
Common Anxiety Medications
- SSRIs (Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors)
- SNRIs (Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors)
- Benzodiazepines (short-term use only)
Pros of Medication
- Can reduce symptoms quickly
- Helpful for severe anxiety or panic attacks
- Improves sleep and physical symptoms
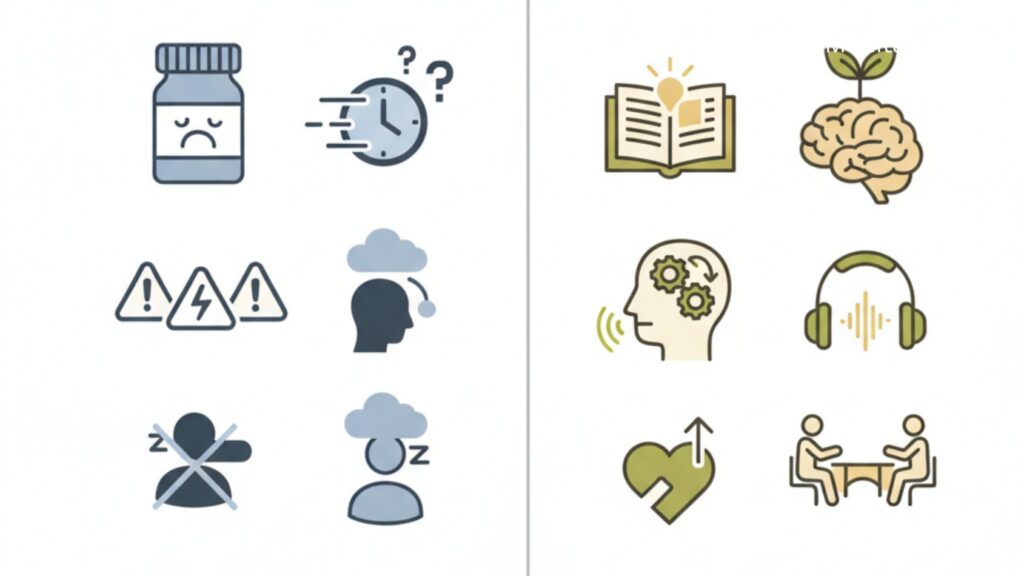
Cons of Medication
- Possible side effects (nausea, dizziness, fatigue)
- Does not address root causes
- Symptoms may return after stopping
Learn more about daily medication use in our article on
Differents Anxiety Medications.

Important: Always consult a licensed healthcare professional before starting or stopping any medication.
Therapy for Anxiety: Benefits and Limitations
Therapy focuses on understanding thoughts, emotions, and behaviors that fuel anxiety. It helps individuals develop coping skills and long-term emotional resilience.
Common Types of Therapy
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
- Exposure Therapy
- Talk Therapy (Psychotherapy)
Pros of Therapy
- Addresses root causes of anxiety
- Long-term improvement
- No medication side effects
Cons of Therapy
- Takes time and consistency
- Requires active participation
- Access and cost may vary
Therapy works especially well when combined with calming daily habits like meditation and breathing. You can explore our
guided meditation for anxiety to support therapy outcomes.
Medication vs Therapy: Key Differences

| Factor | Medication | Therapy |
|---|---|---|
| Speed of relief | Fast | Gradual |
| Long-term benefits | Moderate | High |
| Side effects | Possible | Minimal |
| Root cause treatment | No | Yes |
| Relapse prevention | Limited | Strong |
Which Works Better for Anxiety?
The answer depends on the individual, severity of symptoms, and personal preferences.
- Short-term relief: Medication can help stabilize intense symptoms.
- Long-term recovery: Therapy offers lasting skills and emotional control.
- Best results: Many experts recommend combining medication and therapy.
For mild to moderate anxiety, therapy alone is often effective. For severe anxiety or panic disorders, medication may be used initially alongside therapy.
How to Choose Between Medication and Therapy for Anxiety
Choosing the right anxiety treatment depends on symptom severity, personal preferences, and professional guidance. Follow these steps to make an informed decision.
- Assess the severity of your anxiety
Mild anxiety may improve with therapy alone, while moderate to severe anxiety often benefits from medication, therapy, or a combination of both.
- Consider how long symptoms have lasted
Short-term or situational anxiety may respond well to therapy. Long-lasting or recurring anxiety may require medical support.
- Think about side effects and comfort level
Some people prefer therapy to avoid medication side effects, while others choose medication for faster symptom relief.
- Consult a qualified professional
A licensed therapist or healthcare provider can help determine the most effective and safest treatment option for you.
- Monitor progress and adjust treatment
Regularly review your symptoms and make changes to therapy methods or medication dosage with professional guidance.
What Do Mental Health Experts Recommend?
According to trusted health organizations such as the World Health Organization (WHO), National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH), and NHS, therapy — especially CBT — is considered a first-line treatment for many anxiety disorders.
Medication is recommended when symptoms are intense, persistent, or do not improve with therapy alone.
Authoritative sources:
Can Medication and Therapy Be Used Together?
Yes. Many people benefit from a combined approach. Medication helps stabilize symptoms, while therapy builds long-term coping strategies.
This combination is commonly recommended for panic disorder, PTSD, and chronic anxiety conditions.
Natural and Lifestyle Support for Anxiety
Alongside professional treatment, lifestyle changes can significantly improve anxiety management:
- Daily meditation or mindfulness practice
- Breathing and grounding exercises
- Regular sleep routine
- Reducing caffeine and alcohol
You may find the
3-3-3 rule for anxiety helpful for immediate calming.
Frequently Asked Questions About Medication vs Therapy for Anxiety
Medication and therapy are both effective for treating anxiety, but they work in different ways. Medication can help reduce symptoms quickly, while therapy focuses on understanding triggers and building long-term coping skills. Many people experience the best results when both are combined.
Yes, therapy alone can be very effective, especially for mild to moderate anxiety. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is one of the most researched and effective treatments for anxiety without medication.
Most anxiety medications, such as SSRIs, take about 2 to 6 weeks to show noticeable improvement. Some short-term medications may work faster, but they are usually not recommended for long-term use.
Anxiety medications may cause side effects like drowsiness, nausea, headaches, weight changes, or dependency risks. Side effects vary from person to person, so medical supervision is important.
Yes, combining medication and therapy is commonly recommended for moderate to severe anxiety and is considered safe when guided by healthcare and mental health professionals.
Conclusion
When comparing medication vs therapy for anxiety, there is no one-size-fits-all answer. Medication can offer fast relief, while therapy provides lasting emotional strength and coping skills.
The best approach depends on your symptoms, lifestyle, and professional guidance. With the right support, anxiety can be effectively managed, and a calm, balanced life is possible.
This article is for educational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice.
